The Role of Nutrition in A Healthy Pregnancy
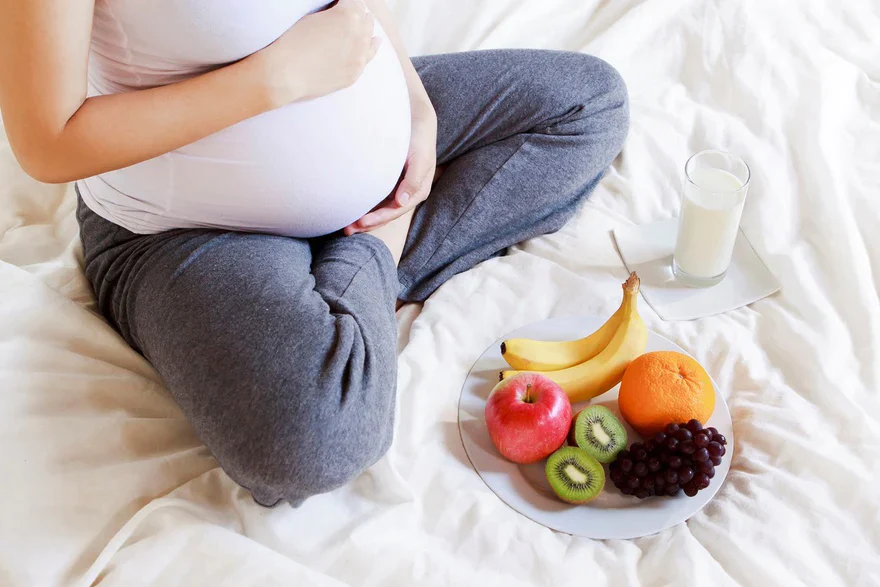

Making good nutrition a crucial component of a successful pregnancy. The involvement of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN) medical experts in helping pregnant mothers achieve optimal nutrition is crucial for the health of both the expectant mother and the growing foetus. We will dig into the relevance of nutrition throughout pregnancy in this in-depth post, highlighting the value of eating a well-rounded meal and the crucial nutrients needed for a healthy pregnancy.
Nutrition and Obetricsst in Perspective
Gynaecology and obstetrics are included under the medical speciality of obstetrics, which is devoted to treating pregnant patients. Gynaecology encompasses the female reproductive system, while obstetrics concerns pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum care. In gynecology & obstetrics, nutrition is crucial, especially during the antenatal (before pregnancy) and prenatal (during pregnancy) phases.
The Benefits of a Healthy Diet
The basis of a good pregnancy is a balanced diet. It gives the woman the vital nutrients she needs to promote the foetus’ growth and development, keep her healthy, and get her body ready for childbirth and breastfeeding. Here are some reasons why a healthy diet is crucial when pregnant:
- Foetal Development: Accelerated foetal growth and development occurs throughout pregnancy. The building blocks for the baby’s body parts, tissues, and bones are provided by proper nourishment. The baby’s brain, spine, and general body structure growth depend on nutrients, including protein, calcium, iron, and folic acid.
- Maternal Health: A mother’s body is under additional strain throughout pregnancy. Her health is supported by nutrient-rich diets, guaranteeing she has the vigour and strength required to bring her pregnancy successfully to fruition. Additionally, typical pregnancy-related problems, including anaemia, insulin resistance, and hypertension, can be avoided or treated with a balanced diet.
- Immune Support: A healthy diet strengthens the mother’s defences against illnesses that might harm her and the unborn child. The body’s defences are strengthened, and general well-being is promoted by consuming enough vitamins and minerals.
Pregnancy Complications Associated with Malnutrition
- Low Birth Weigh and Prematurity: Pregnancy malnutrition can impair foetal development and result in premature or small newborns. Infants with low birth weight are more likely to have health issues such as respiratory distress, infections, and delays in growth. Malnutrition can also result in premature delivery, which raises the risk of newborn problems.
- Neural Tube abnormalities: A growing foetus may acquire neural tube abnormalities if critical nutrients like folic acid are not consumed sufficiently. Lifelong problems result from these severe birth abnormalities that impact the brain, vertebral column, or spine. It’s essential to ensure your diet is balanced and includes foods and supplements high in folate.
- Maternal Survival Risks: Pregnancy malnutrition harms the foetus and jeopardises the mother’s health. Anaemia, premature delivery, preeclampsia, and infections are all more likely to affect pregnant women who aren’t getting enough nourishment. These issues with maternal health might harm the mother’s long-term health and the pregnancy.
Vital Foods for Pregnant Women
During pregnancy, a few essential nutrients are extremely important. These consist of:
- Folic Acid: This vitamin is crucial in the first trimester because it protects the growing baby’s head and spine against neural tube abnormalities. As advised by medical professionals, leafy greens, lentils, enriched grains, and tablets are foods high in folic acid.
- Iron: Pregnancy-related iron deficiency anaemia is a prevalent worry, thus lean meats, chicken, fish, and legumes. And fortified cereals are crucial sources of iron. To maintain the mother’s and foetus’s health, obstetricians regularly check iron levels.
- Calcium: Calcium plays a crucial role in the growth of a baby’s teeth and bones. Additionally, it supports the mother’s bone condition. In addition to dairy items, green leafy veggies, and fortified diets, OB-GYN specialists may provide vitamins as appropriate.
- Protein is essential for the embryo’s placenta and the developing baby’s tissues to grow. Excellent protein sources include nutritious meats, fish, seafood, poultry, dairy goods, legumes, and nuts. Pregnant women are frequently advised to consume enough protein to assist foetal growth by obstetricians and gynaecologists.
- Omega-3 Fatty Compounds: It is crucial for an infant’s eyes and brain and may be sourced from fatty fish, linseed and walnuts. Specialists in OB-GYN may recommend suitable supplements and food sources to guarantee a sufficient intake of essential fatty acids.
- Supplements and Minerals: Gynae and obstetrics professionals frequently advise prenatal supplements comprising key nutrients like A, C, D, and E vitamins, as well as zinc and magnesium, to address any nutritional shortages and support the wellness of the mom and baby.
Individualised Dietary Plans
Obstetricians and gynaecologists know that every pregnancy is different and every pregnant woman has different dietary demands. They are essential in creating individualised dietary regimens depending on the expectant mother’s age, weight, history of illness, and any particular issues associated with her pregnancy. Regular OB-GYN visits offer a chance to assess nutritional status, make any corrections, and handle any issues that could arise throughout pregnancy.